In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on finding sustainable alternatives to traditional packaging materials. Molded pulp has emerged as a promising solution, offering a versatile, eco-friendly, and biodegradable packaging option for various industries. This article explores the concept of molded pulp, its manufacturing process, its applications, and its potential to shape a greener future for packaging.
Understanding Molded Pulp
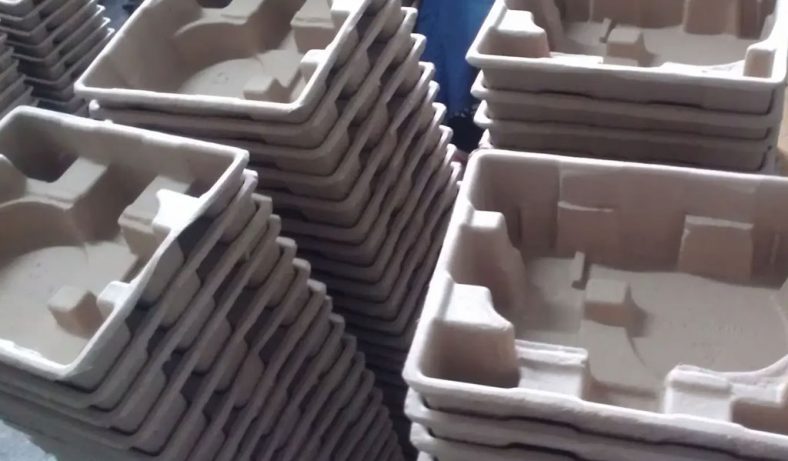

What is Molded Pulp?
Molded pulp, also known as molded fiber, is a form of biodegradable packaging material made from recycled paper waste. The process of creating molded pulp involves blending paper fibers with water to create a slurry.
This slurry is then shaped into various forms using molds and subsequently dried and hardened. The result is a lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly material that can be used for various packaging purposes.
Historical Development of Molded Pulp
The concept of molded pulp dates back to the early 20th century when it was first used for packaging egg cartons. Over time, advancements in technology and increased environmental awareness have led to the development of more sophisticated molded pulp manufacturing processes. This section will delve into the evolution of molded pulp and its transition from simple egg cartons to a wide range of applications.
Manufacturing Process
Raw Materials Used in Molded Pulp
The foundation of molded pulp lies in its raw materials. This section will discuss the types of paper waste used, including recycled newspapers, cardboard, and other post-consumer materials. Additionally, the significance of sourcing sustainable raw materials and its impact on the overall environmental footprint of molded pulp will be explored.
The Production Process
The production process of molded pulp involves several key stages, including pulping, molding, drying, and finishing. Each step contributes to the final quality of the molded pulp product. In this section, we will break down each stage of the manufacturing process and discuss the machinery and technologies used to create molded pulp packaging.
Advancements in Molded Pulp Manufacturing
With increasing demand for sustainable packaging, manufacturers have been investing in research and development to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the molded pulp production process. This section will highlight some of the recent advancements and innovations in the industry.
Moulds & Dies For Molded Pulp
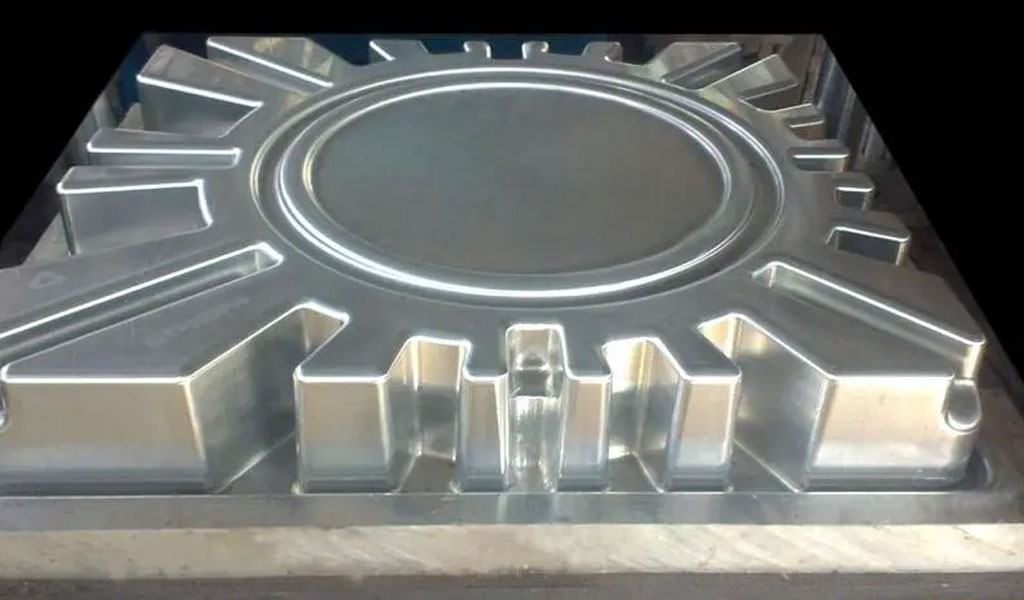
Molds and dies play a crucial role in the manufacturing process of molded pulp products. They are essential tools used to shape the pulp slurry into specific forms, creating the final product with precision and consistency. In this section, we will explore the importance of molds and dies in molded pulp production and their impact on product quality, design flexibility, and overall efficiency.
Role of Molds and Dies in Molded Pulp Production
Molds and dies are instrumental in converting the pulp slurry into desired shapes, ranging from simple designs like egg cartons to intricate structures used in consumer electronics packaging. The primary functions of molds and dies in molded pulp production include:
- a. Shaping: Molds and dies are used to shape the wet pulp slurry into the desired configuration. The unique design of each mold determines the final appearance and functionality of the molded pulp product.
- b. Uniformity: Consistency is vital in mass-produced items. Molds and dies ensure that each molded pulp item conforms to the same specifications, ensuring uniformity and meeting quality standards.
- c. Precision: Well-crafted molds and dies ensure that the final product meets the required dimensional tolerances and specifications. This is particularly important for products like electronic devices, which need precise fits and protection.
- d. Reproducibility: Molds and dies allow for the efficient reproduction of molded pulp products in large quantities, making it a cost-effective solution for industries with high-volume production needs.
Design Flexibility with Molds and Dies
The versatility of molded pulp products largely depends on the design flexibility offered by molds and dies. Manufacturers can create custom molds and dies to produce a wide range of shapes and sizes, tailored to specific product requirements. This design flexibility makes molded pulp an attractive option for various industries, as it can be adapted to suit the unique needs of different products.
Mold and die design considerations include:
- a. Product Functionality: The design of the mold and die must align with the functional requirements of the final product. For example, protective packaging for delicate electronics may require specific cushioning features.
- b. Aesthetics: Molds and dies can be crafted to create visually appealing molded pulp products, enhancing their marketability and branding potential.
- c. Sustainable Packaging: Molds and dies can help optimize material usage, minimizing waste and contributing to the eco-friendliness of the packaging.
Types of Molds and Dies for Molded Pulp
There are two main types of molds used in molded pulp production:
- a. Wet Press Molds: Wet press molds, also known as water molds, are typically used for products that require a smooth surface finish, such as plates or trays. The wet pulp is placed in the mold, excess water is drained, and pressure is applied to compress the fibers and create the desired shape.
- b. Dry Press Molds: Dry press molds are used for products that need a textured surface, like egg cartons or beverage carriers. The wet pulp is pressed between male and female molds to remove excess water and create the final form.
Material Considerations for Molds and Dies
The choice of materials for molds and dies is essential in ensuring their longevity and performance. Common materials used for molds and dies in molded pulp production include:
- a. Metal: Metal molds, often made from aluminum or stainless steel, are durable and capable of withstanding the rigors of high-volume production.
- b. Plastic: Plastic molds and dies can be a cost-effective option for smaller production runs. However, they may wear out faster than metal counterparts.
- c. Composite Materials: Some manufacturers use composite materials that offer a balance of durability and cost-effectiveness.
Advancements in Mold and Die Technology
As the demand for molded pulp products continues to rise, advancements in mold and die technology have been made to improve efficiency and productivity. These advancements include:
- a. Computer-Aided Design (CAD): CAD software enables precise and intricate mold designs, allowing manufacturers to create complex shapes and optimize material usage.
- b. 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, have opened up new possibilities in mold and die production, reducing lead times and costs for prototyping.
- c. CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has enhanced the precision and quality of molds and dies, resulting in more consistent and higher-quality products.
Molds and dies are integral components in the molded pulp production process. Their design and material choices significantly influence the versatility, quality, and cost-effectiveness of the final products. As technology continues to evolve, molds and dies will play an increasingly vital role in the advancement and widespread adoption of molded pulp as a sustainable packaging solution across various industries.
Environmental Impact
The Sustainability of Molded Pulp
Molded pulp is considered one of the most sustainable packaging materials available. This section will discuss the environmental benefits of using molded pulp, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower energy consumption, and decreased waste to landfills.
Biodegradability and Compostability
One of the standout features of molded pulp is its biodegradability. This section will explore how molded pulp products break down naturally and can be composted, further minimizing their impact on the environment.
Applications of Molded Pulp
Food Packaging
Molded pulp is used extensively in food packaging applications. From egg cartons to takeaway containers, this section will delve into how molded pulp provides a safe and sustainable option for transporting and storing food products.
Electronics and Technology Packaging
With its cushioning and shock-absorbing properties, molded pulp has found applications in electronics and technology packaging. This section will discuss how it protects fragile devices during transit and reduces electronic waste.
Medical and Healthcare Industry
Molded pulp is also making strides in the medical and healthcare industry due to its ability to provide hygienic, sterile, and eco-friendly packaging for medical instruments and supplies.
Sustainable Consumer Products Packaging
Molded pulp has gained popularity as a packaging material for consumer products like cosmetics, personal care items, and home goods. We will explore the advantages of using molded pulp for branding and marketing sustainable products.
Challenges and Future Outlook
- Challenges Facing Molded Pulp Industry:Despite its numerous benefits, the molded pulp industry faces certain challenges that hinder its widespread adoption. This section will address issues such as scalability, cost, and competition with other packaging materials.
- The Future of Molded Pulp : Looking ahead, the future of molded pulp appears promising. In this section, we will discuss potential innovations, collaborations, and market opportunities that could further establish molded pulp as a mainstream packaging solution.
In conclusion, molded pulp has emerged as a sustainable and versatile packaging material with the potential to revolutionize the industry. Its eco-friendly properties, biodegradability, and wide range of applications make it a strong contender in the quest for greener packaging solutions. As consumer and industry demands for sustainable practices continue to rise, molded pulp stands ready to play a vital role in shaping a more environmentally conscious future.









